By Group "Human Superintelligence"
Abstract
In recent years, the fluctuations in the gold price have always been the focus of numerous investors and market analysts. The core objective of our research is to deeply explore the correlation between gold price fluctuations and market sentiment. This research on the correlation not only helps investors better understand the mechasim of gold price formation, but also provides a unique perspective and valuable data support for macroeconomic research.
During the research process, data collection is of utmost importance. This blog showcases the entire process of using Python for web crawling and downloading text data. In order to obtain comprehensive and representative data, we selected The New York Times and the Reddit forum as the sources of text data. As a globally renowned media, The New York Times has in-depth and extensive coverage of various economic events and market dynamics. The Reddit forum, on the other hand, gathers users from all over the world. They share their views and discussions on a wide range of topics on the forum, including the gold market.
Web Scraping on The New York Times
1. Importing Required Libraries and Setting Up the NYT API
We started by importing the necessary libraries to support the script's functionality: requests for making API calls, pandas for managing and organizing data, datetime for parsing and formatting dates, and newspaper for scraping and extracting the content of news articles. Once the tools were in place, we configured the NYT API by setting up the API key, endpoint, and query parameters. These parameters included a search keyword "gold price", a specified date range, and a sorting preference to ensure the fetched news articles were relevant and focused. This setup allowed us to efficiently retrieve gold-related news articles from The New York Times API, laying the groundwork for further data processing and analysis.
import requests
import pandas as pd
from datetime import datetime
from newspaper import Article
# Replace with your New York Times API key
API_KEY = "your API_KEY"
# Set API endpoint and parameters
base_url = "https://api.nytimes.com/svc/search/v2/articlesearch.json"
params = {
"api-key": API_KEY,
"q": "gold price", # Search keyword
"begin_date": "statr_date", # Start date
"end_date": "end_date", # End date
"sort": "relevance" # Sort by relevance
}
2. Crawling and Saving Gold Matket News from the API
We sent a GET request to the NYT API to fetch gold-related news articles. If the request was successful, we parsed the JSON response into a Python dictionary, allowing us to easily access and manipulate the data for further processing and analysis. This step was crucial for extracting structured information from the API response and preparing it for storage and analysis.
# Send GET request
response = requests.get(base_url, params=params)
response.raise_for_status() # Check if the request was successful
data = response.json()
We designed the script to iterate through the list of articles returned in the API response. For each article, we extracted the publication date and formatted it into a more readable YYYY-MM-DD format. This step ensured that the dates were standardized and easier to work with during subsequent data analysis and storage.
# Parse the returned data
for result in data.get("response", {}).get("docs", []):
# Handle datetime format
pub_date = result.get("pub_date", "")
try:
# Attempt to parse datetime
parsed_date = datetime.strptime(pub_date, "%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S+0000")
formatted_date = parsed_date.strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
except ValueError:
# If parsing fails, use a default value or skip
formatted_date = "Unknown date"
We utilized the newspaper library to download and parse the full text of each article from its URL. This allowed us to extract the complete content of the articles for deeper analysis. If the download or parsing failed due to issues like invalid URLs or network errors, we implemented a fallback mechanism that used a placeholder message ("Failed to retrieve content") to ensure the script continued running smoothly without interruption.
# Get article content
article_url = result.get("web_url", "")
try:
# Use the newspaper library to fetch the article
article = Article(article_url)
article.download()
article.parse()
article_content = article.text
except Exception as e:
article_content = "Failed to retrieve content"
Then we organized the key details of each article—such as the title, abstract, publication date, URL, and content—into a structured dictionary. This dictionary was then appended to the news_data list, creating a centralized and organized collection of all the extracted article information. This approach allowed us to efficiently manage and prepare the data for further processing, such as saving it to a CSV file or performing analysis.
article_data = {
"title": result.get("headline", {}).get("main", "No title"), # Title
"abstract": result.get("abstract", "No abstract"), # Abstract
"published_date": formatted_date, # Publication date
"url": article_url, # URL
"content": article_content # Article content
}
news_data.append(article_data)
| Variable | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| title | The article's headline. |
| abstract | A brief summary of the article. |
| published_date | The formatted publication date. |
| url | The URL of the article. |
| content | The main text content of the article. |
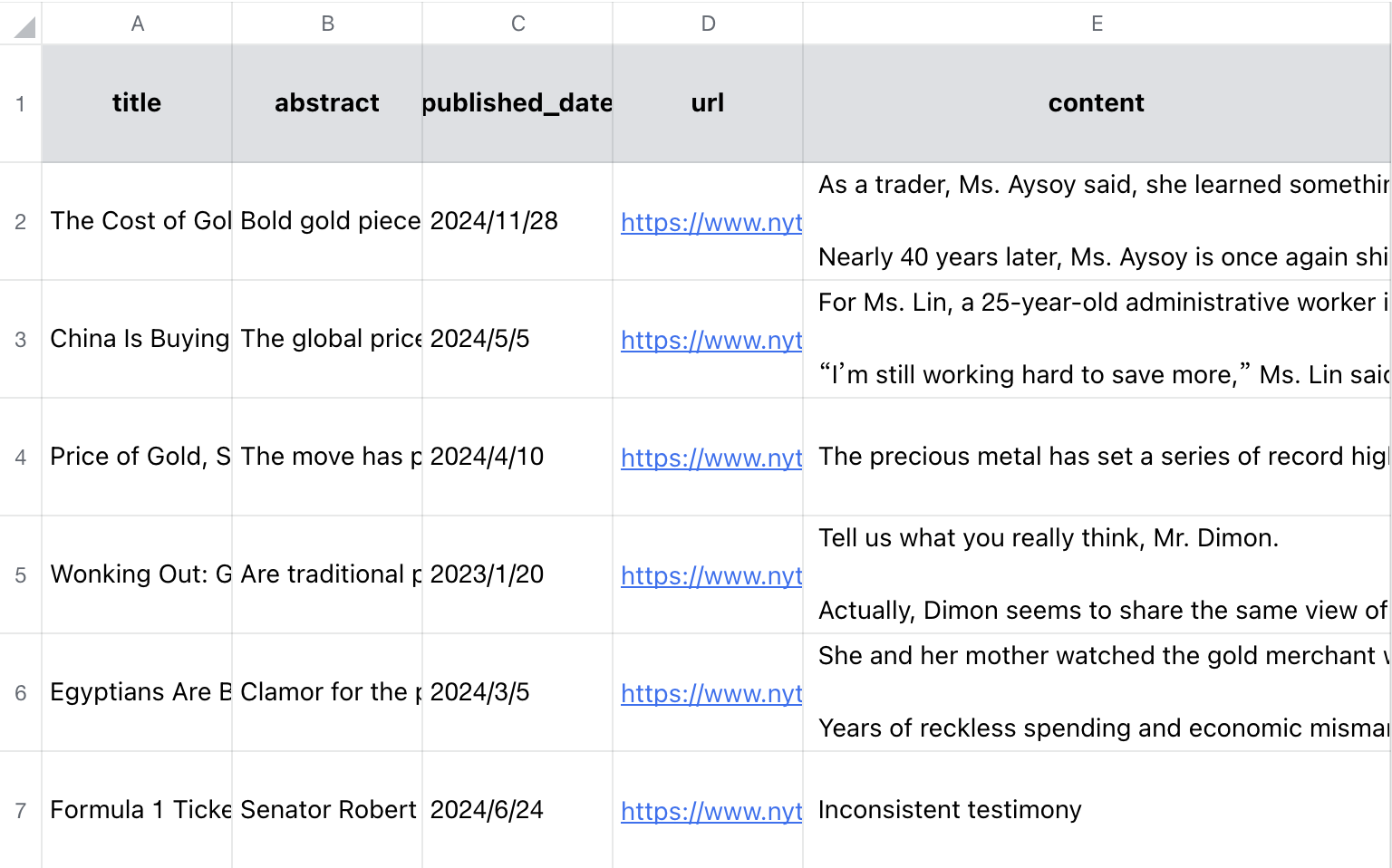
Here is a presentation of the text data results from 2023-2024:
Web Scraping on Reddit
1. Importing PRAW and Setting Up the Reddit API
We also collected text data from the Reddit forum. We selected three subreddits, namely "r/gold", "r/investment", and "r/personalfinance", as the sources of the text data. In these subreddits, we used "gold price" as the search keyword to search for posts, comments, and replies on comments.
Before crawling text data, we need to create a Reddit account and import the PRAW package. Then we apply an API from preferences (reddit.com)and establish a connection with the Reddit forum.
PRAW, an acronym for "Python Reddit API Wrapper", is a Python package that allows for simple access to Reddit's API. PRAW aims to be easy to use and internally follows all of Reddit's API rules. With PRAW there's no need to introduce sleep calls in your code. Give your client an appropriate user agent and you're set.
import praw
import pandas as pd
import time
# Set up Reddit API client
reddit = praw.Reddit(client_id='client_id',
client_secret='client_secret',
user_agent='user_agent')
2. Crawling Data and Variable Interpretation
We have written the following function get_posts. By default, it can crawl the top 10 posts under the subreddit_name and the search keyword topic, as well as the top 20 comments of each post and the replies to each comment.
When crawling the data, we focused on the comments and the replies to the comments, rather than the content of the posts themselves. This is because some posts are too long, and only several sentences in them reflect the author's views and attitudes. This will lead to a large amount of crawled data, most of which are invalid texts. In contrast, the comment section has more user participation. The opinions in the comments are often more genuine, unadorned, and concise , which makes it convenient for us to collect market sentiment information with higher density and quality.
In addition, we also pay attention to the scores of comments and replies, which are obtained by subtracting the number of downvotes from the number of upvotes for that comment or reply. A higher score often reflects that the content of the comment is of higher quality and has a higher level of community recognition. Since only a part of users will leave comments, while another part of the users just browse and upvote without making comments, comments with high scores can better represent the emotions of the community users. In our subsequent analysis of market sentiment, we can assign higher weights to comments with high scores.
def get_posts(subreddit_names, topic, limit=10, comment_limit=20):
posts = []
# Loop through each subreddit
for subreddit_name in subreddit_names:
subreddit = reddit.subreddit(subreddit_name)
print(f"Scraping subreddit: {subreddit_name}")
for post in subreddit.search(topic, limit=limit):
post_info = {
'subreddit': subreddit_name,
'title': post.title,
'score': post.score,
'created_utc': post.created_utc,
'comments': []
}
# Load all comments (excluding nested replies)
post.comments.replace_more(limit=0)
for comment in post.comments[:comment_limit]: # Keep the top comments
comment_info = {
'body': comment.body,
'score': comment.score,
'replies': []
}
# Fetch replies to the comment, sort by score, and keep top 5
comment.replies.replace_more(limit=0)
top_replies = sorted(comment.replies, key=lambda x: x.score, reverse=True)[:5]
for reply in top_replies:
reply_info = {
'body': reply.body,
'score': reply.score
}
comment_info['replies'].append(reply_info)
post_info['comments'].append(comment_info)
posts.append(post_info)
return posts
We selected three subreddits, namely "r/gold", "r/investment", and "r/personalfinance", as the sources of text data. This is because these three subreddits have more followers, and when using "gold price" as the search keyword, a large number of posts and replies can be retrieved.
# Set search keywords
subreddit_names = ['gold','investing', 'personalfinance'] # List of subreddits to scrape
topic = 'gold price'
posts = get_posts(subreddit_names, topic, limit=200, comment_limit=50)
Here shows the results of the text data from Reddit:
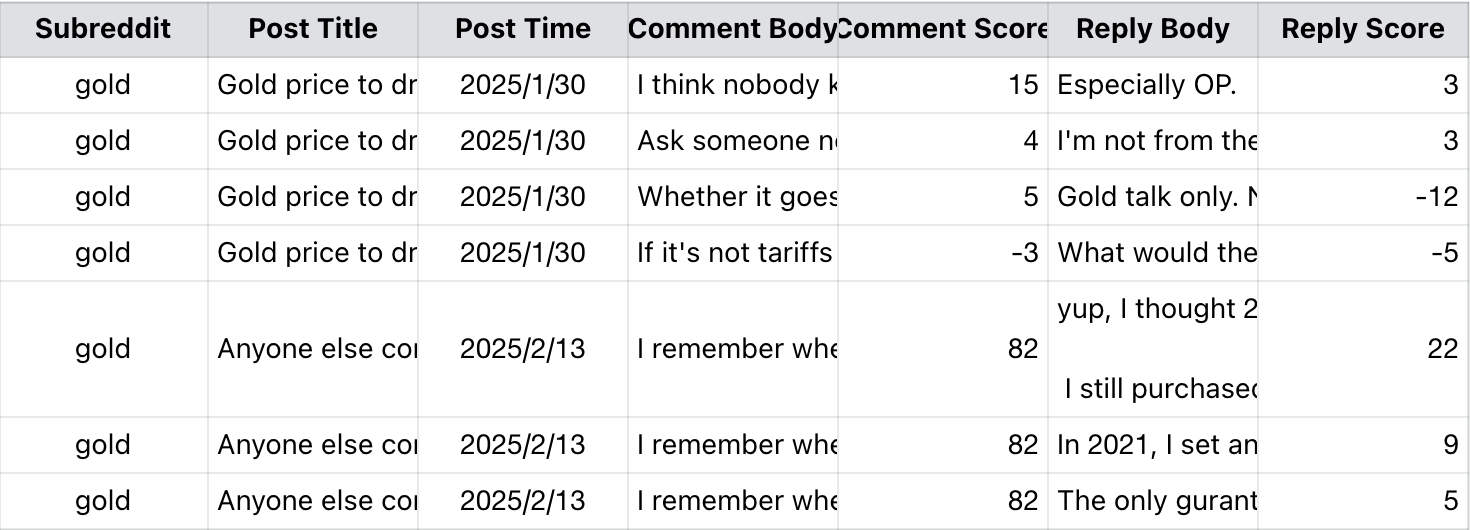
The interpretations of each variable in the text data are as follows.
| Variable | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Subreddit | The name of the subreddit forum. |
| Post Title | The title of the post. |
| Post Time | The specific moment when a post is actually published on the Reddit. |
| Comment Body | The actual textual content of a comment in response to a post. |
| Comment Score | The net popularity or approval level of a comment. |
| Reply Body | The actual textual content of a reply in response to a comment. |
| Reply Score | The net popularity or approval level of a reply. |
The following is the code for storing the text data.
# Prepare comments data for DataFrame
comments_data = [
(post['subreddit'],
post['title'],
time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d', time.localtime(post['created_utc'])),
comment['body'],
comment['score'],
reply['body'],
reply['score']
)
for post in posts
for comment in post['comments']
for reply in comment['replies']
]
# Create DataFrame
df_comments = pd.DataFrame(comments_data, columns=[
'Subreddit',
'Post Title',
'Post Time',
'Comment Body',
'Comment Score',
'Reply Body',
'Reply Score'
])
# Display the DataFrame
print(df_comments)
# Save to CSV file (optional)
df_comments.to_csv('reddit_comments_with_replies.csv', index=False, encoding='utf-8')
Problems We Solved
1. Choosing Between NYT Article API and Google News
In the process of building a gold market sentiment analysis system, crawling news data is a crucial step. Initially, we faced two main choices: NYT Article API and Google News. After in-depth analysis and practical testing, we ultimately chose the NYT Article API as our primary data source. Below is our thought process and rationale for this decision.
Our goal was to crawl gold-related news data spanning from 2014 to 2024, a period of ten years. This extensive time frame meant the data volume would be massive and complex. If we chose Google News as the data source, despite its wide coverage, its search results are often too vast and fragmented, making it highly prone to triggering 429 errors (Too Many Requests). Such errors not only interrupt the crawling process but also add extra processing costs and time consumption.
In contrast, the NYT Article API provides a more centralized data source. As one of the world's most authoritative media outlets, The New York Times offers news coverage with high credibility and representativeness, better reflecting the sentiment changes in the gold market. Additionally, the API's design allows us to effectively avoid 429 errors by rationally planning request frequencies and crawling in batches.
The quality of news data directly impacts the accuracy of subsequent analysis. While Google News has extensive coverage, its search results include a large amount of news from unverified sources and duplicate content, making data cleaning and filtering a significant challenge. On the other hand, the NYT Article API provides data from a single, authoritative source, ensuring the reliability and consistency of news content. This is particularly important for our analysis of gold market sentiment, as reports from authoritative media often better reflect the true sentiment and trends of the market.
2. Error Handling
The inclusion of Error Handling is aimed at enhancing the program's robustness and reliability, ensuring that the program does not crash when encountering issues such as failed network requests, data parsing exceptions, or other unexpected errors. Instead, it captures errors and provides clear prompts. By addressing exceptions such as network issues, API limits, date format errors, and article retrieval failures, the error handling mechanism ensures the program can operate stably in complex environments, while also improving user experience and code maintainability.
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print("Network request error:", e)
except Exception as e:
print("Other error:", e)