By Group 4
Seeking Alpha is a website that provides financial analysis and stock ideas. In this project, we use Beautiful Soup to webscrape stock ideas on Seeking Alpha in the past three months in the healthcare industry.
Import libraries
import requests
import re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import time
Obtain urls for all articles
To webscrape the long ideas and news on Seeking Alpha, we first need to obtain the urls for all articles. We use the url for the contents page as the starting point.
The contents page of the long ideas and news on Seeking Alpha is as follows:
We use the requests to request the html of the contents page. Then, we use the Beautiful Soup to parse the html and obtain the urls suffix for each article, and save the urls in a list.
lst_url = 'https://seekingalpha.com/stock-ideas/healthcare' # url for the contents page
r_lst = requests.get('https://seekingalpha.com/stock-ideas/healthcare') # request the html
s_lst = BeautifulSoup(r_lst.text,'lxml') # parse the html
lst = [] # create an empty list to store the urls
for item in s_lst.find_all('a',{"data-test-id":"post-list-item-title"}): # find all the articles
address = item.get('href') # get the url suffix for each article
lst.append(address) # append the url suffix to the list
Define functions to obtain the data we need
We define the following functions to obtain the data we need: 1. get_text: to obtain the text of each article 2. get_time: to obtain the time of each article 3. get_stock: to obtain the stock mainly discussed in each article 4. get_follower: to obtain the number of followers of the writer 5. get_like: to obtain the number of likes of each article
def get_text(s):
text = ''
for i in s.find_all('p'):
text = text + i.get_text()
return text
def get_time(s):
for x in s.find_all('meta',property = 'article:published_time'):
time = x.get('content')
return time
def get_stock(s):
p1 = re.compile(r'[(](.*?)[)]', re.S) # to obtain the content in the brackets
try:
return re.findall(p1,str(s.find('a',{"class":"xs-YW"})))[0] # to obtain the stock
except:
return
def get_follower(s):
try:
return s.find('div',{"class":"tF-RY aw-gT aw-g7 aw-hm rT-Si ag-gn aw-gT aw-g7 aw-hm"}).get_text().split()[0]
except:
return 0
def get_like(s):
p1 = re.compile(r'[(](.*?)[)]', re.S) # to obtain the content in the brackets
try:
return re.findall(p1,str(s.find('span',{"class":"wS-jk"})))[0] # to obtain the number of likes
except:
return 0
Some points to note: 1. We use the try and except function to skip the articles that do not have the data we need, or else the program will stop running. 2. Regular expression is to obtain the number of likes of each article, because the number of likes is in the format of 'Like (1)', and we only need the number 1. 3. Find text in
tag rather than get text in the whole html, because the main text of each article is in the
tag. 4. To find specific content, we can find the corresponding tags and class by using the inspect function in the browser. 5. To achieve the same function as the inspect function, we can use the find_all function, and specify the class using a dictionary.
Obtain and save data we need
In this part, we add 'https://seekingalpha.com' to the each url suffix we obtained in the previous part to request the html of each article, and parse the html to obtain the data we need. Then, we write the data to a csv file.
In the request part, to avoid the risk of being blocked by the website, we do the following: 1. We use a for loop to request the html of each article one by one. 2. We set the timeout to 10 seconds, and use the time library to set a sleep time of 1 second between each request. 3. We also use the try and except function to avoid the risk of being blocked by the website.
header = ['stk','time','text','followers','likes']
with open('/Users/file/text.csv','a', encoding = 'UTF8', newline = '' ) as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
writer.writerow(header)
for address in lst:
try:
time.sleep(random.random()) # set a sleep time of 1 second between each request
r = requests.get('https://seekingalpha.com' + address, timeout = 10) # request the html
s = BeautifulSoup(r.text,'lxml') # parse the html
text = get_text(s) # get the text
time = get_time(s) # get the time
stk = get_stock(s) # get the stock
follow = get_follower(s) # get the number of followers
like = get_like(s) # get the number of likes
writer.writerow((stk,time,text,follow,like)) # write the data to the csv file
except:
pass
f.close()
Now the data we need is saved in the csv file, the format is as follows:
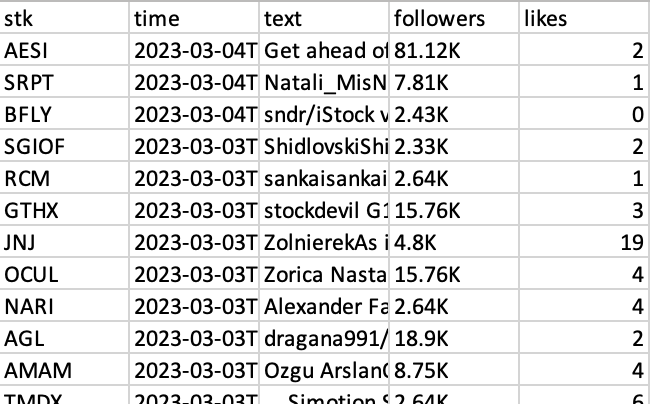
The next step is to clean the data and do some analysis. Thanks for reading!