By Group "NLP Intelligence"
This post aims to show some difficulties met when scraping the website 'www.zacks.com' and our solutions.
How to scrape all pages when searching for many keywords
We tried different keywords in the search bar of Zacks and found the patterns of the weblinks returned. For example, if you enter 'PDD'(the ticker of a China Concept Stock), click 'search' button and then choose the second page of all search results, the weblink will be https://www.zacks.com/stock/research/PDD/all-news?page=2. So, the keyword and the page number are both included in the link. Besides, we also find that each page will provide 25 search records, so we can use another layer of loop to get information from record 1 to record 25.
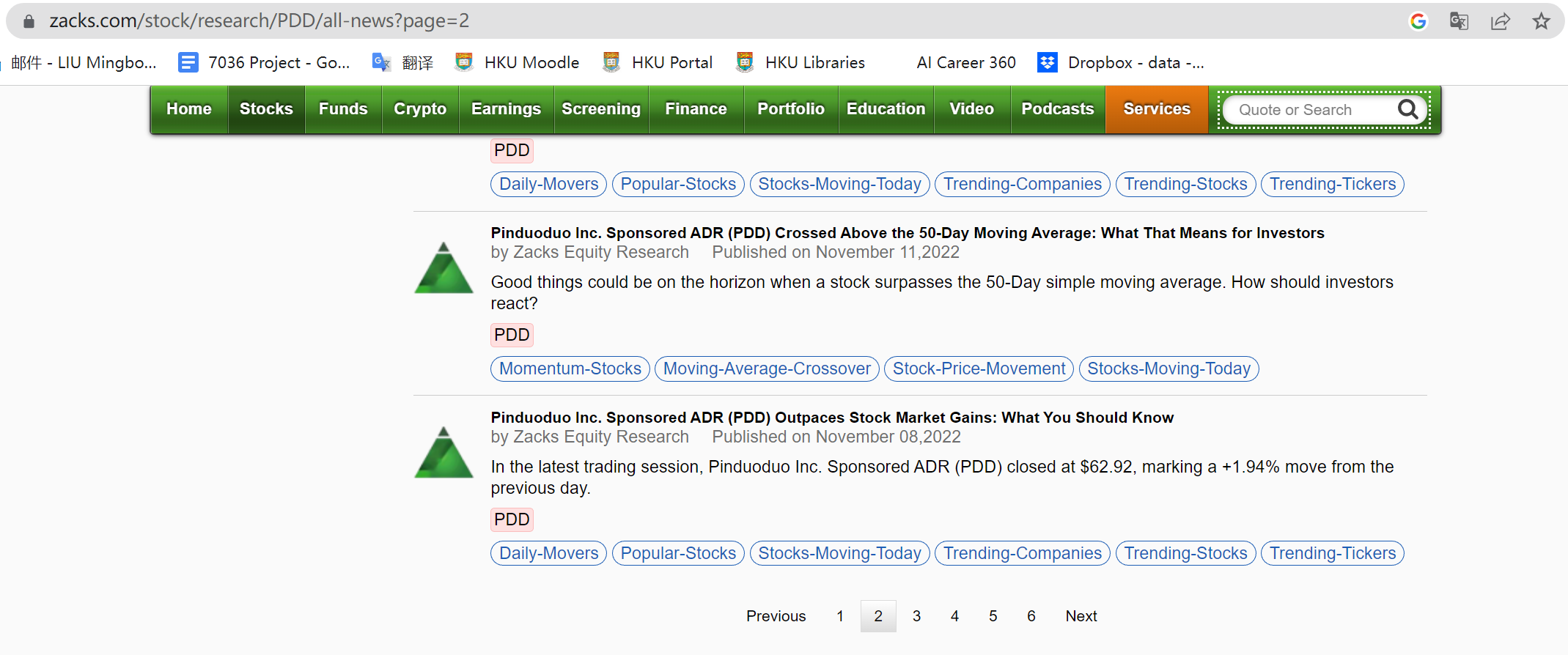
We can use the following code to loop through all pre-defined keywords and all pages:
search_text=['put in your keyword list']
for i in range(len(search_text)):
page=1
try:
while True:
url = r'https://www.zacks.com/stock/research/{}/all-news?page={}'.format(search_text[i], page)
browser.get(url)
for j in range(1,26):
try:
'''
where you locate the elements you need
'''
except:
print('cannot find row {} on page {} of {}'.format(j, page,search_text[i]))
raise No_Next_Line()
else:
page += 1
except:
The code snippet includes three layers of loop. When there's no next page for current searching keyword, we need to break out of the inner two layers to create a new url.
We can do this by defining an exception class and raise it in the outer loop:
class No_Next_Line(Exception):
pass
for i in range(len(search_text)):
try:
'''
two inner loops, where you raise the exception
when conditions are fulfilled
'''
except No_Next_Line:
print('No next page')
pass
How to change time strings to datetime object
When we try to clean the data, another problem occured. The publish time data is recorded in string format(such as 'Published on December 23,2022'), and it's hard to apply filters to it. So, we convert it to datetime object and set the time span:
Date_to_change = author_Time.split('on ')[-1].replace(',','/') #change time info formati into 'March 22/2022'
Date = dt.date(int(Date_to_change.split('/')[-1]), list(calendar.month_name).index(Date_to_change.split(' ')[0]), int(Date_to_change.split('/')[0][-2:])) #such as dt.date(2022, 3, 22)
#apply filters
if Date>dt.date(2022,6,30):
continue
elif Date<dt.date(2020,6,30):
raise No_Next_Line()
else:
output_df.append([Headline,author_Time,Link_to_Source,Date])
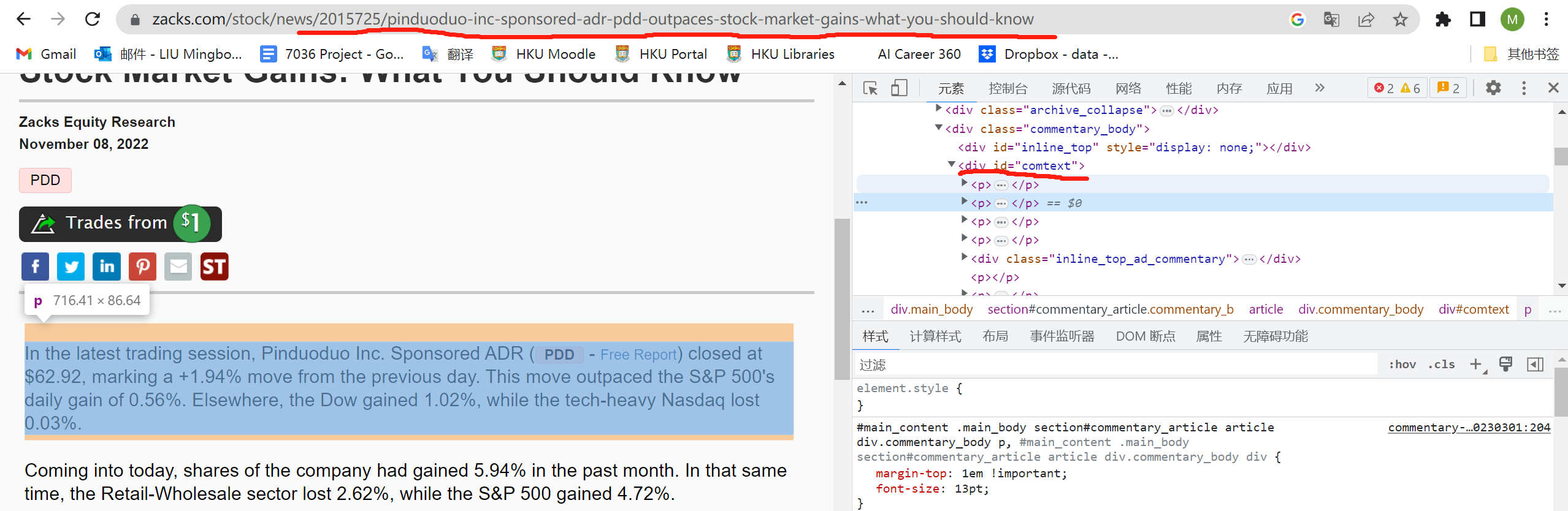
How to capture main content of the selected news
The weblink of a specific piece of news contains title (such as https://www.zacks.com/<br/>commentary/1853617/bear-of-the-day-gds-holding-gds), so we cannot use for loops for all news. We looked into the links scraped from the search result page and use beautiful soup to extract the main content:
Link_to_Source = browser.find_element("xpath", "/html/body/div[5]/div[3]/div[2]/section/div[1]/div/div/div[{}]/h3/a".format(j)).get_attribute('href')
text_list=[]
for link in list(output_df['Link_to_Source']):
url=link
browser.get(url)
soup=BeautifulSoup(browser.page_source,'lxml')
main_text=soup.find("div",attrs={"id":"comtext"}).get_text()
text_list.append(main_text)
output_df['Content']=text_list
Fight against timeouts
One important method to avoid timeouts is to add random sleep, though decreasing the performance:
time.sleep(np.random.uniform(1, 2))